Peter Lynch, the legendary manager of the Magellan Fund at Fidelity Investments from 1977 to 1990, achieved impressive returns averaging 29.2% annually. His success made him one of the most respected figures in the world of investing, and his approach has been widely studied. Lynch’s investment strategy is based on a combination of simplicity, diligent research, and a focus on finding “good stories” in the stock market. Here are the core principles of his investment philosophy:
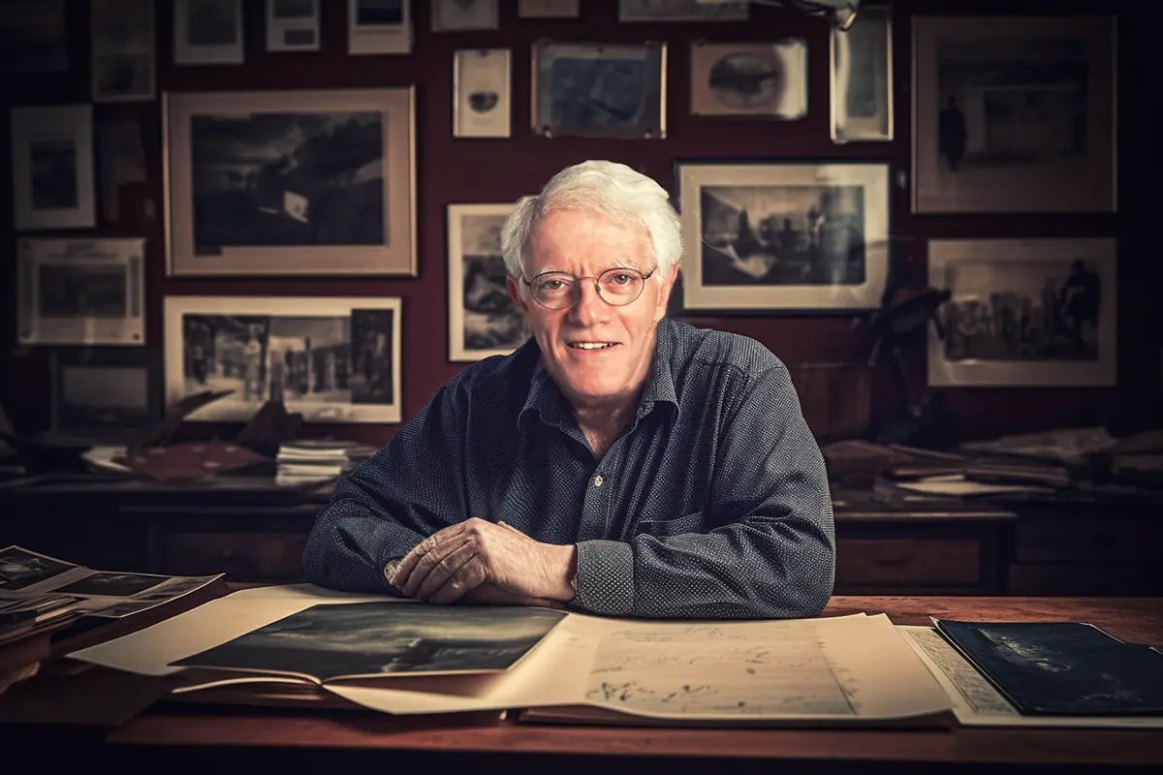

1. Invest in What You Know
- Lynch famously advocated for investing in industries or products that investors personally understand. He believed individual investors could gain an edge by identifying trends and companies they encounter in everyday life. This “buy what you know” approach allows investors to recognize opportunities in sectors they are familiar with.
2. Conduct Thorough Research
- While Lynch encouraged investing in familiar businesses, he emphasized the importance of deep research. He suggested understanding the company’s fundamentals, business model, competitive advantages, and financial health before making any investment decision. He relied heavily on metrics like the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio to determine if a stock was over or undervalued.
3. Classify Stocks into Categories
- Lynch categorized stocks into six types: slow growers, stalwarts, fast growers, cyclicals, asset plays, and turnarounds. Each category has distinct investment characteristics, risks, and potential returns. Understanding which category a stock falls into helps investors set realistic expectations and manage risks accordingly.
4. Focus on Growth Stocks with Reasonable Valuations
- Lynch was known for his focus on growth stocks, particularly those that demonstrated strong earnings growth potential. However, he cautioned against paying too high a price for growth, emphasizing a reasonable P/E ratio relative to growth rate (PEG ratio). He believed in paying fair prices for quality growth rather than chasing “hot” stocks at any cost.
5. Look for Companies with Strong Earnings Growth
- Lynch favored companies with a history of consistent and sustainable earnings growth. This metric indicates the company’s ability to generate profits and reinvest in its future, increasing the likelihood of long-term appreciation in stock value.
6. Stay Patient and Think Long-Term
- Lynch’s strategy involved patience and a long-term mindset. He believed in holding stocks for several years to allow their growth potential to materialize. His motto, “time, not timing, is the key to building wealth in the stock market,” reflects his belief in staying invested for the long haul rather than attempting to time the market.
7. Avoid “Diworsification”
- Lynch coined the term “diworsification” to describe over-diversifying, which can dilute an investor’s focus and returns. He believed in focusing on a manageable number of high-quality stocks rather than spreading investments too thinly across various sectors or companies, which can reduce the potential for meaningful gains.
8. Watch for Red Flags
- Lynch advised watching out for red flags such as excessive debt, weak cash flow, or unsustainable growth rates. He believed these indicators could signal trouble for a company’s future performance. Staying vigilant about these warning signs helps investors avoid potential pitfalls.
9. Learn from Mistakes
- Peter Lynch stressed that mistakes are an inevitable part of investing, but learning from them is crucial. He recommended maintaining a record of investment decisions to help identify patterns, improve judgment, and develop a more disciplined approach to investing.
10. Stay Informed and Adapt
- Lynch was a proponent of continuous learning, stressing the need to stay updated on economic trends, market shifts, and individual company developments. His approach encouraged investors to remain adaptable and open to new investment opportunities while managing risks.





 Long-Term Success:
Long-Term Success: 


 Nelson Rolihlahla
Nelson Rolihlahla 








 Baiju Prafulkumar Bhatt, an American entrepreneur of Indian descent, has left an indelible mark on the financial technology landscape as the co-founder of Robinhood, a leading US-based financial services company. Born in 1984 or 1985, Bhatt spent his formative years in Poquoson, Virginia, as the son of Indian immigrants. He embarked on his academic journey at Stanford University, where he earned a bachelor’s degree in physics and subsequently completed a master’s degree in mathematics in 2008. It was during his time at Stanford that Bhatt crossed paths with his future business partner,
Baiju Prafulkumar Bhatt, an American entrepreneur of Indian descent, has left an indelible mark on the financial technology landscape as the co-founder of Robinhood, a leading US-based financial services company. Born in 1984 or 1985, Bhatt spent his formative years in Poquoson, Virginia, as the son of Indian immigrants. He embarked on his academic journey at Stanford University, where he earned a bachelor’s degree in physics and subsequently completed a master’s degree in mathematics in 2008. It was during his time at Stanford that Bhatt crossed paths with his future business partner,
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/13874040/stevejobs.1419962539.png)
