Table of Contents
ToggleCOMPANY CHART
COMPANY FINANCIALS DATA
COMPANY NEWS
COMPNAY HISTORY AND FOUNDING DAYS
Introduction
Tencent Holdings Ltd. is a giant in the technology world. Since its start in 1998, Tencent has grown to be one of the biggest companies globally. It is known for its work in social media, entertainment, fintech, and cloud computing. This article will explore Tencent’s history, its founders, major stakeholders, and the latest news about the company.
Founding and Early Years
Tencent was founded in November 1998. The founders are Ma Huateng (Pony Ma), Zhang Zhidong (Tony Zhang), Xu Chenye, Chen Yidan, and Zeng Liqing. The company started with OICQ (Open ICQ), an instant messaging service. This service later became QQ, which became very popular and helped Tencent succeed early on.
Founders
-
Ma Huateng (Pony Ma): Ma Huateng is the chairman and CEO of Tencent. He is the most well-known founder. Under his leadership, Tencent grew from a messaging service to a tech giant.
-
Zhang Zhidong (Tony Zhang): Zhang Zhidong was the chief technology officer (CTO) until 2014. He helped build Tencent’s technology systems.
-
Xu Chenye: Xu Chenye is one of the co-founders. He has helped with Tencent’s investment strategies.
-
Chen Yidan: Chen Yidan focused on Tencent’s growth in various sectors, like education and philanthropy.
-
Zeng Liqing: Zeng Liqing helped with Tencent’s early operations and business plans.
Major Stakeholders
Over the years, Tencent’s ownership has changed. Here are the major stakeholders:
-
Naspers Limited/Prosus N.V.: This South African company, through its subsidiary Prosus, owns a large part of Tencent. They first invested in Tencent in 2001, and it has been very profitable.
-
Founders and Executives: The founders and senior executives still own a significant part of Tencent.
-
Institutional Investors: Many global investors, like mutual funds and pension funds, own shares in Tencent because of its strong performance.
-
Public Shareholders: Tencent is publicly traded on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. This means many people worldwide own shares in the company.
Milestones and Latest Developments
Early 2000s: Growth and New Products
After QQ’s success, Tencent started offering more services. They launched QQ Game, a large online gaming platform, and QQ.com, a web portal.
2011: WeChat Launch
In 2011, Tencent launched WeChat (Weixin). This mobile app started as a messaging service but grew to include social networking, payments, e-commerce, and more. WeChat’s all-in-one approach was groundbreaking.
2018: Global Investments
Tencent expanded globally by investing in other companies. Notable investments include stakes in Epic Games, Tesla, and Spotify. These investments helped Tencent integrate new technologies and content.
2020-2023: Challenges and Innovations
Recent years brought both challenges and opportunities. Tencent faced regulatory scrutiny in China, affecting its gaming and fintech operations. Despite this, Tencent continued to innovate in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and international markets.
Latest Developments in 2024
-
Metaverse Projects: Tencent is developing the Metaverse, investing in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies. These projects aim to create immersive digital experiences.
-
Sustainability Efforts: Tencent aims to be carbon neutral by 2030. They are investing in renewable energy and green technologies to fight climate change.
-
Healthcare and Biotechnology: Tencent is focusing more on healthcare. They are using technology to advance digital health solutions and investing in biotech startups.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Tencent is working to meet regulatory standards by improving compliance frameworks and engaging with authorities. This ensures their operations are sustainable.
Conclusion
Tencent’s journey from a messaging service to a global tech leader is impressive. The vision of its founders and the company’s ability to adapt have driven its success. As Tencent faces new challenges and opportunities, its focus on innovation and sustainability will likely keep it at the forefront of the tech industry.
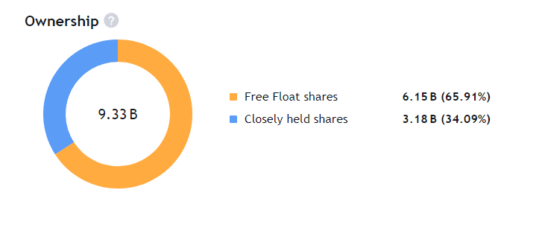
OWNERSHIP STRUCTURE
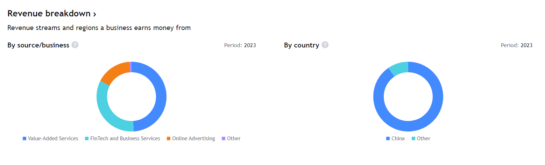
REVNUE BRAKDOWN
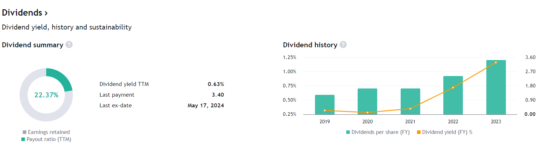
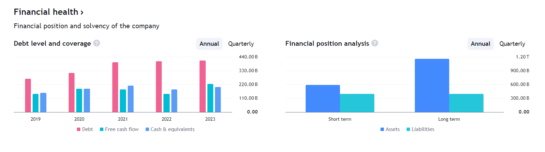
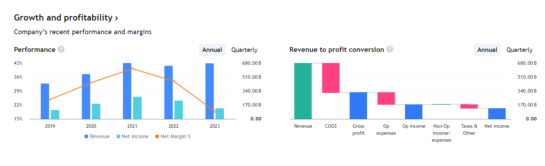

ALL THE CHARTS FROM TRADING VIEW
Financial Data
<td
| Year | 2017 | Dec 2017 | 2018 | Dec 2018 | 2019 | Dec 2019 | 2020 | Dec 2020 | 2021 | Dec 2021 | 2022 | Dec 2022 | 2023 | Dec 2023 | TTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total revenue (B HKD) | 274.16 | +54.43% | 370.37 | +35.09% | 427.81 | +15.51% | 541.69 | +26.62% | 675.06 | +24.62% | 644.88 | -4.47% | 672.96 | +4.35% | 674.86 |
| Cost of goods sold (B HKD) | -139.33 | -204.74 | -239.79 | -297.51 | -384.95 | -374.27 | -355.34 | -345.25 | |||||||
| Gross profit (B HKD) | 134.82 | +39.47% | 165.63 | +22.85% | 188.02 | +13.52% | 244.18 | +29.87% | 290.11 | +18.81% | 270.61 | -6.72% | 317.62 | +17.37% | 329.61 |
| Operating expenses (excl. COGS) (B HKD) | -58.46 | -75.18 | -82.92 | -109.07 | -150.90 | -151.04 | -145.93 | -143.81 | |||||||
| Operating income (B HKD) | 76.36 | +30.96% | 90.45 | +18.45% | 105.10 | +16.20% | 135.11 | +28.55% | 139.21 | +3.03% | 119.57 | -14.11% | 171.69 | +43.59% | 185.80 |
| Non-operating income, total (B HKD) | 24.41 | 19.68 | 20.85 | 63.05 | 179.58 | 143.65 | 0.17 | 2.18 | |||||||
| Pretax income (B HKD) | 100.77 | +59.24% | 110.13 | +9.28% | 125.96 | +14.37% | 198.16 | +57.33% | 318.79 | +60.87% | 263.22 | -17.43% | 171.85 | -34.71% | 187.98 |
| Equity in earnings (B HKD) | 0.95 | 1.76 | -1.91 | 4.13 | -19.82 | -18.76 | 6.41 | 8.60 | |||||||
| Taxes (B HKD) | -18.15 | -17.15 | -15.32 | -22.36 | -24.41 | -25.02 | -47.82 | -50.19 | |||||||
| Non-controlling/minority interest (B HKD) | -1.11 | -1.50 | -2.92 | -0.31 | -3.60 | -0.54 | -3.13 | -3.32 | |||||||
| Net income before discontinued operations (B HKD) | 82.46 | 93.24 | 105.81 | 179.62 | 270.96 |
