- Geography: China is the world’s fourth-largest country by land area, with diverse geographical features including mountains, plateaus, deserts, and plains. Major landmarks include the Himalayas, the Gobi Desert, the Yangtze River, and the Great Wall of China.
- History: China has one of the world’s oldest civilizations, with a recorded history dating back over 5,000 years. It has been ruled by various dynasties and empires, experiencing periods of great prosperity and cultural achievement. In 1949, the Communist Party of China (CPC) established the People’s Republic of China.
- Government: China is a one-party socialist state governed by the Communist Party of China (CPC). The President serves as the head of state, while the Premier is the head of government. The National People’s Congress is the highest organ of state power.
- Economy: China has the world’s second-largest economy by nominal GDP and is the largest manufacturing and exporting nation. Over the past few decades, it has experienced rapid economic growth, fueled by manufacturing, exports, and investments. China is also a major importer of commodities.
- Culture: Chinese culture is rich and diverse, encompassing various traditions, customs, and arts. It has made significant contributions to literature, philosophy, art, music, cuisine, martial arts, and technology. Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism have been influential philosophies.

- Population: China is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.4 billion people. The country faces demographic challenges such as an aging population and gender imbalance due to the one-child policy, which has been relaxed in recent years.
- Technological Advancements: China has become a global leader in technology and innovation, with significant investments in areas such as artificial intelligence, renewable energy, telecommunications, and space exploration. Companies like Huawei, Alibaba, and Tencent have gained international prominence.
- Foreign Policy: China’s foreign policy is characterized by its emphasis on sovereignty, territorial integrity, and non-interference. It seeks to expand its influence through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and has become increasingly assertive in regional and global affairs.
- Challenges: China faces challenges such as environmental pollution, income inequality, corruption, human rights abuses, and tensions with neighboring countries over territorial disputes, particularly in the South China Sea.
Day: April 20, 2024
ASIA
Asia is the world’s largest and most populous continent, covering an area of about 44.58 million square kilometers and home to over 4.6 billion people, constituting roughly 60% of the world’s population. Here are some key points about Asia: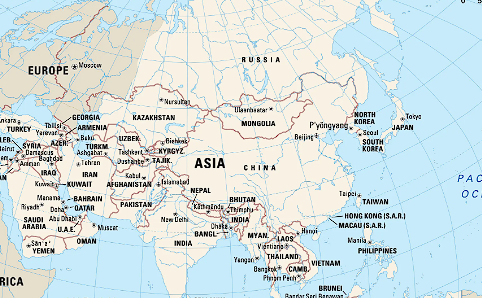
- Geography: Asia is incredibly diverse geographically, featuring vast plains, high mountain ranges, deserts, and extensive coastlines. It includes major geographical features such as the Himalayas, the Gobi Desert, the Siberian tundra, and the fertile river valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates, the Yangtze, and the Ganges.
- Cultural Diversity: Asia is incredibly diverse culturally, with numerous languages, religions, and ethnic groups. It is the birthplace of major religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and Confucianism, as well as the origin of many ancient civilizations, including those of Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley, and China.
- Economic Powerhouse: Asia is an economic powerhouse, with some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, including China, India, Japan, and South Korea. The region is a hub for manufacturing, trade, and innovation and plays a significant role in the global economy.
- Political Landscape: Asia is home to a wide range of political systems, from authoritarian regimes to democracies. Countries like China, North Korea, and Iran have authoritarian governments, while others like India, Japan, and South Korea have democratic systems.
- Global Influence: Asia’s influence extends beyond its borders, impacting global politics, economics, and culture. Countries like China and India are increasingly asserting themselves on the world stage, shaping global trends and influencing international relations.

- Challenges: Asia faces numerous challenges, including poverty, inequality, environmental degradation, and political instability. Issues such as territorial disputes, nuclear proliferation, and terrorism also pose significant challenges to regional stability.
- Technological Advancements: Asia is a leader in technological innovation, with countries like Japan, South Korea, and China making significant advancements in fields such as electronics, robotics, and artificial intelligence.
- Regional Cooperation: Despite historical tensions and conflicts, there are efforts towards regional cooperation in Asia. Organizations like the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) aim to promote economic integration and political dialogue among Asian countries.
IRAN
Iran, officially known as the Islamic Republic of Iran, is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered to the northwest by Armenia and Azerbaijan, to the north by the Caspian Sea, to the northeast by Turkmenistan, to the east by Afghanistan and Pakistan, to the south by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, and to the west by Turkey and Iraq.
Here are some key points about Iran:
- History: Iran has a rich history dating back thousands of years, with significant contributions to art, science, and culture. It was home to one of the world’s earliest civilizations, the Elamite, and later became part of the Persian Empire, one of the largest empires in history.
- Culture: Iranian culture is diverse, with influences from various civilizations and ethnic groups. Persian literature, poetry, and art have had a profound impact globally. Iran is known for its rich tradition of poetry, with poets like Rumi and Hafez being revered internationally.
- Religion: Iran is an Islamic republic, with Islam being the dominant religion. The majority of Iranians are Shia Muslims, though there are also Sunni Muslims, Christians, Jews, and other religious minorities.
- Politics: Iran’s political system is unique, combining elements of an Islamic theocracy with a republican democracy. The Supreme Leader holds significant power, with the President serving as the head of government. The country has faced international scrutiny over its human rights record and its nuclear program.
- Economy: Iran has a mixed economy, with significant government involvement in key sectors such as energy and finance. Its economy relies heavily on oil and gas exports, though efforts have been made to diversify in recent years. Economic sanctions have significantly impacted Iran’s economy.
- International Relations: Iran’s relations with other countries have been complex. It has had strained relationships with the United States and some Western countries, particularly over issues such as its nuclear program and support for militant groups. However, it maintains close ties with countries like Russia and China.

- Nuclear Program: Iran’s nuclear program has been a source of international concern and controversy. While Iran claims its program is for peaceful purposes, such as energy production, many countries, particularly Western powers, suspect it of seeking to develop nuclear weapons.
- Recent Developments: Iran has been involved in various regional conflicts, including the Syrian Civil War and the conflict in Yemen. It has also faced internal challenges, including protests over economic issues and political repression.
Documentary Video
What we know about Israel’s missile attack on Iran
US officials say Israel hit Iran with a missile in the early hours of Friday, in what appears to have been a retaliatory strike after weeks of escalating tensions between the two countries.
There are competing claims about the scale of the attack on the Isfahan region and the extent of any damage, with Iranian state media downplaying its significance.
It comes after weeks of soaring tensions between the regional rivals, which have already seen an Israeli attack on an Iranian compound in Syria, and Iran launch an unprecedented assault against Israel.
Here is everything we know about the latest incident so far.
How do we know there has been a strike?
Israel does not routinely confirm its military actions, which have targeted Iranian-backed armed groups in Syria and Iraq on many occasions.
However, US officials have confirmed to the BBC’s partner CBS News that an Israeli missile did hit Iran.
US sources say a missile was involved in the attack, while Iran says it involved small drones.
Iran’s government tightly controls access to the country. The BBC does not have direct access to the central region of Isfahan, where this incident played out overnight.
What weapon may have been used?
So far, there has been a lot of speculation regarding the type of missile used.
BBC Verify has tried to identify the weapon by analysing images of wreckage posted from an area in neighbouring Iraq, 60km (45 miles) south-west of the capital Baghdad.
 Sabreen News
Sabreen NewsAmong experts, there now seems to be a wider consensus in thinking that a two-stage missile was used – and was probably air-launched. Many identify the debris with Israeli-produced Blue Sparrow missiles.
Justin Crump, a former British Army officer who runs risk intelligence company Sibylline, agreed that the debris seen in the pictures was probably from a missile booster “with the warhead having detached and presumably gone on to achieve its mission – this is the motor which falls to earth”.
“The booster has attachment points typically used to connect to an aircraft and its general size suggests it may have been an air-launched system,” Crump said.
Although we cannot yet independently verify the exact type of missile, it is known that Israel has developed this type of weapon.
“Israel has previously used such weapons in Syria, so this is well within their capabilities,” Crump added.
What is Iran saying about the strike?
Some Iranian officials and media have confirmed there was an attempted strike but are downplaying the significance of it. There have been no reports of casualties.
Iran’s Fars news agency says explosions were heard near an army base and air defence systems were activated.
Explosions heard in the Isfahan area were “due to air defence firing at suspicious objects” and there was no damage, a state media channel quoted a general as saying.
 IRIB
IRIBThe semi-official Tasnim news agency, which is close to the powerful Islamic Revolution Guard Corps military wing, posted a video of a nuclear facility in Isfahan which did not show any signs it had been hit.
The International Atomic Energy Agency has confirmed there was no damage to Iran’s nuclear sites.
Hossein Dalirian, a spokesman for Iran’s National Centre of Cyberspace, said there had been “no air attack from outside borders”.
He said Israel had “only made a failed and humiliating attempt to fly quadcopters [drones]” which had been shot down.
Iran imposed restrictions on commercial flights in the hours immediately after the strike but they have now been lifted.
Explosions were also reported overnight in Iraq and Syria – where armed groups backed by Iran operate – but it is unclear if they were directly linked to the Isfahan strike.
The Syrian defence ministry said an air defence site in the south of Syria had been hit by an Israeli missile in the early hours of Friday morning local time. Israel has not confirmed it was behind the strike.
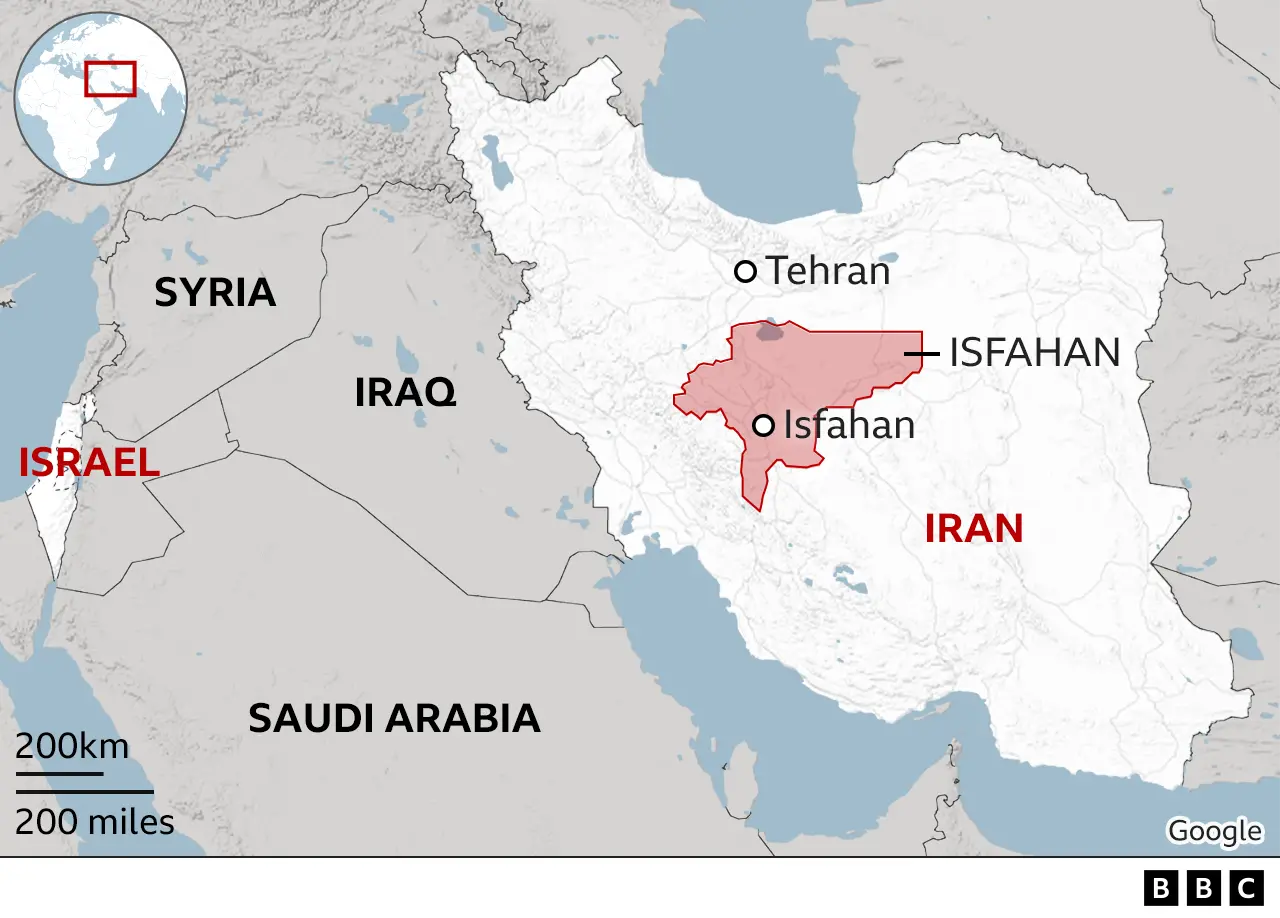
Why was Isfahan targeted and why now?
Isfahan province is a large area in the centre of Iran which takes its name from its largest city.
The region is home to significant Iranian military infrastructure, including a large air base, a major missile production complex and several nuclear facilities.
Israel would usually tell the US in advance about military action, but Italy’s foreign minister Antonio Tajani told reporters at the G7 meeting in Capri that Washington had only been “informed at the very last minute”.
Speaking at the summit, US Secretary of State Antony Blinken refused to be drawn on the attack, saying only that the US had “not been involved in any offensive operations”.
This latest strike comes less than a week after Iran launched hundreds of missiles and drones at Israel, an incident seen as a dramatic escalation in tensions.
Despite its vast scale and unprecedented nature, Iran’s attack was largely unsuccessful, with the vast majority of projectiles shot down by Israeli air defences with the help of the US, UK and other allies.
That unprecedented attack on Israeli soil was in response to a strike against a building on an Iranian diplomatic compound in Syria on 1 April.
Israel has not publicly confirmed it was behind that strike either, but it is widely accepted that it was.


Will this increase tensions between Israel and Iran?
The full significance of this latest strike is still becoming clear and it is not yet known whether Iran will seek to respond.
BBC security correspondent Frank Gardener describes the scale of Friday’s attack as limited and potentially designed to ensure the conflict goes no further.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu will come under competing pressures from some of his own generals and political allies to push back against Iran, according to BBC international editor Jeremy Bowen.
 EPA
EPAIsrael has come under huge international pressure from the US and other Western allies not to take any action which risks turning the long-running proxy war between the two Middle East rivals into a direct conflict.
This flare-up in hostilities comes against the backdrop of the war in Gaza, where the Israeli military is fighting Iran-backed Hamas.
What has the reaction in Israel and around the world been?
Some of the responses from within Israel have highlighted the country’s political divisions.
Ultranationalist Security Minister Itamar Ben Gvir described the strike on Iran as “feeble” or “lame”.
In response, Israeli opposition leader Yair Lapid called for him to be sacked, and said his remark had ridiculed and embarrassed Israel.
The UK government said it would not speculate on the strike, but said Israel should avoid “significant escalation” while exercising its “right to self-defence”.
European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen called on all sides to refrain from further action.
How has the world economy reacted?
There are concerns a worsening conflict in the Middle East could disrupt oil supplies.
Brent crude, the international benchmark for oil prices, rose by 1.8% to $88 a barrel after the attack.
Oil prices had jumped by as much as 3.5% initially but the price stabilised when it became clearer the strike was limited.
The price of gold – which is often seen as a safe investment at times of uncertainty – briefly came close to a record high before falling back to nearly $2,400 an ounce.


