Discovering the Magic: A Journey through Disneyland
Nestled in the heart of Anaheim, California, Disneyland stands as a beacon of enchantment and wonder, drawing millions of visitors from around the globe each year. Since its opening in 1955, this iconic theme park has been captivating guests of all ages with its blend of imagination, storytelling, and innovation. Let’s embark on a journey through the history, attractions, and enduring charm of Disneyland.
A Land of Dreams: The Birth of Disneyland
Conceived by Walt Disney as a place where families could escape the ordinary and immerse themselves in a world of fantasy, Disneyland opened its gates on July 17, 1955. Walt’s vision was to create a theme park unlike any other, one where guests could step into their favorite fairy tales, explore distant lands, and experience the magic of Disney animation.
The park was divided into themed “lands,” each offering its own unique atmosphere and attractions. Main Street, U.S.A. welcomed visitors with a nostalgic trip back in time to turn-of-the-century America, while Adventureland, Frontierland, Fantasyland, and Tomorrowland promised adventures beyond imagination.
Classic Attractions and Timeless Magic
From the moment guests step foot inside Disneyland, they are greeted by a wealth of iconic attractions that have become synonymous with the park’s legacy. In Fantasyland, visitors can board the whimsical “it’s a small world” boat ride, journey into the heart of a diamond mine on the exhilarating “Snow White’s Enchanted Wish,” or take flight with Peter Pan on the enchanting “Peter Pan’s Flight.”
Adventure seekers can explore the treacherous waters of the Jungle Cruise, embark on a swashbuckling adventure with Pirates of the Caribbean, or traverse the perilous peaks of the Matterhorn Bobsleds. Meanwhile, in Tomorrowland, guests can blast off to outer space on Space Mountain, pilot their own spacecraft on Astro Orbiter, or explore the galaxy at Star Wars: Galaxy’s Edge.
Evolution and Expansion
Over the years, Disneyland has evolved and expanded, introducing new attractions, lands, and experiences while preserving the timeless charm that has made it a beloved destination for generations. In 2001, Disney California Adventure Park opened adjacent to Disneyland, offering a celebration of California’s rich history and culture.
Recent additions, such as Star Wars: Galaxy’s Edge and Pixar Pier, have further enhanced the park’s offerings, immersing guests in the worlds of their favorite films and characters like never before. Whether building a droid in Black Spire Outpost or racing through the Incredicoaster, Disneyland continues to push the boundaries of imagination and storytelling.
The Magic Lives On
As Disneyland approaches its 70th anniversary, its magic shows no signs of fading. Generations of families have made cherished memories within its gates, from first-time visits with wide-eyed children to nostalgic returns for adults who grew up with the park. Disneyland’s enduring appeal lies in its ability to transport guests to a world where dreams come true, where the magic of childhood is celebrated, and where anything is possible.
In a fast-paced world filled with technological marvels and digital distractions, Disneyland remains a beacon of innocence, joy, and wonder—a place where the young and the young at heart can come together to laugh, play, and create memories that will last a lifetime. As Walt Disney himself once said, “Disneyland will never be completed. It will continue to grow as long as there is imagination left in the world.” And so, the magic of Disneyland lives on, inspiring dreamers and believers for generations to come.
Referance:CHATGPT






























 In the dynamic world of financial markets, traders constantly seek tools that can help them make informed decisions amidst volatility. Among the plethora of strategies and methodologies, technical analysis stands out as a popular approach. Technical indicators, in particular, play a crucial role in helping traders identify trends, gauge market sentiment, and time their trades effectively. Here, we delve into the ten best technical indicators that traders rely on for success.
In the dynamic world of financial markets, traders constantly seek tools that can help them make informed decisions amidst volatility. Among the plethora of strategies and methodologies, technical analysis stands out as a popular approach. Technical indicators, in particular, play a crucial role in helping traders identify trends, gauge market sentiment, and time their trades effectively. Here, we delve into the ten best technical indicators that traders rely on for success.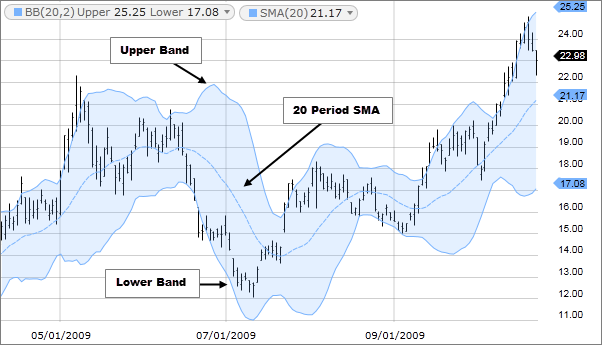
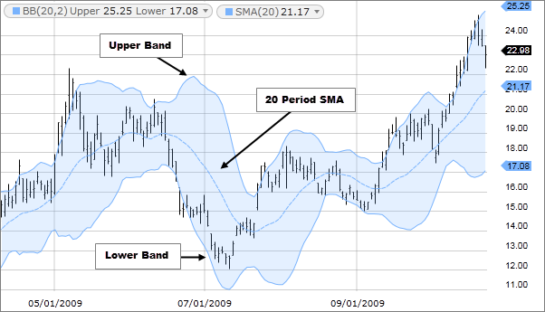
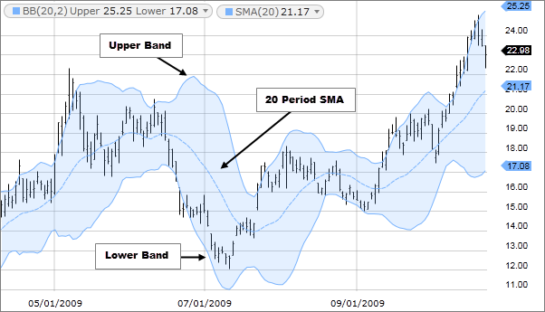
 Simple Moving Average (SMA): SMA calculates the average price of a security over a specific period, equally weighting each data point.
Simple Moving Average (SMA): SMA calculates the average price of a security over a specific period, equally weighting each data point.
 JPMorgan Chase & Co.
JPMorgan Chase & Co.

 As it prepares to move into its new headquarters at 270 Park Avenue in 2025,
As it prepares to move into its new headquarters at 270 Park Avenue in 2025,